What Does Carbon Credit Exchanges Do?
Carbon Credit Exchanges Do
Carbon credits are used to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to the goals of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs). They are sold as a form of financial instrument that allows individuals, businesses, and corporations to offset their carbon emissions. They are available in different currencies, such as US dollars, euros, Australian dollars, and GBP. There are many factors that affect the price of carbon credits. For instance, where the project is located and its delivery date will affect the cost. Also, the volume of credits traded at any given time can have an impact on the prices.
Carbon trading has become popular among both individuals and organizations. Companies and governments have begun using the carbon market as a way to offset their emissions. As a result, the number of carbon credit exchange has grown. However, many of them are still in their infancy. Some exchanges are based on digital technology, while others are run by a compliance system regulator.
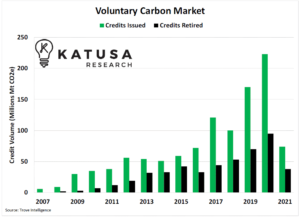
There are two main types of carbon credit exchanges. The first is the voluntary market, which aims to meet international climate goals. Its products are based on specific standards and have limited regulatory oversight. Its members include airlines, oil and gas majors, and tech companies.
What Does Carbon Credit Exchanges Do?
The voluntary market does not have a cap on the number of tons of emissions. In fact, more and more industry sectors are aiming for net-zero goals. In addition, the value of these products is stabilized by government regulation. It is not a free market, as there are rules of supply and demand that will push up the prices.
On the other hand, the compliance market has a cap on the amount of emissions that are allowed. It also requires verification of the projects. For example, large wind turbines will not allow credits for a certain period of time. In contrast, industrial projects, which typically have a higher volume of credits, will be easier to certify.
Tokenization of carbon credits is an important step in the process of promoting liquidity in the carbon market. They are stored on a blockchain, which ensures that each token follows the same standard. This helps the market to be transparent and secure.
The carbon exchanges will also offer an option to sell carbon credits directly to companies. This will help the sale of large-scale carbon projects. Generally, the market for these kinds of credits will be led by multinational corporations, but individuals and communities will also have the opportunity to participate.
In order to avoid cheating, it is important that carbon projects are governed by legal and regulatory requirements. They must also provide additional social and environmental benefits. It is common for community-based projects to generate more co-benefits than industrial ones. These credits trade at a premium, especially if the project is part of the UN SDGs.
There are also a number of carbon brokers, which act as intermediaries between companies and the carbon market. They buy credits from retailers and then sell them to end buyers. They receive commission in return. These companies often also have a carbon project development arm.